-
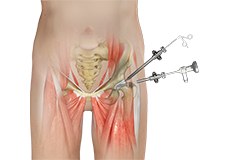
Hip Arthroscopy
Hip arthroscopy, also referred to as keyhole or minimally invasive surgery, is a procedure in which an arthroscope is inserted into your hip joint to check for any damage and repair it simultaneously.
-
Osteoarthritis of the Hip
Osteoarthritis, also called degenerative joint disease, is the most common form of arthritis. It occurs most often in the elderly. This disease affects the tissue covering the ends of bones in a joint called cartilage.
-
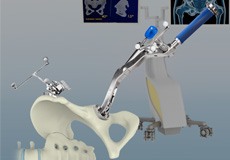
Computer Navigation for Total Hip Replacement
For a successful total hip replacement, accurate positioning of the implants is crucial to accomplish a good clinical outcome. Computer-navigated total hip replacement is an advanced technology developed to provide more accurate positioning of an implant.
-
Revision Total Hip Relacement
During total hip replacement, the damaged cartilage and bone are removed from the hip joint and replaced with artificial components. At times, hip replacement implants can wear out for various reasons and may need to be replaced with the help of a surgical procedure known as revision hip replacement surgery.
-
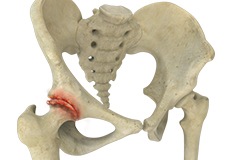
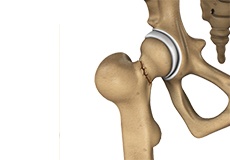
Hip Fracture
The hip joint is a “ball and socket” joint. The “ball” is the head of the femur or thighbone, and the “socket” is the cup-shaped acetabulum. The joint surface is covered by a smooth articular surface that allows pain-free movement in the joint.
-
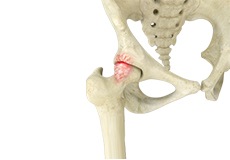
Avascular Necrosis
Avascular necrosis, also called osteonecrosis, is a condition in which bone death occurs because of inadequate blood supply to it. Lack of blood flow may occur when there is a fracture in the bone or a joint dislocation that may damage nearby blood vessels.
-
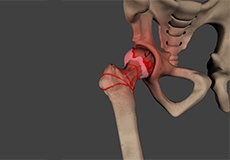
Femoro Acetabular Impingement
Femoroacetabular impingement (FAI) is a condition characterised by excessive friction in the hip joint from the presence of bony irregularities. These cause pain and decreased range of hip motion.
-
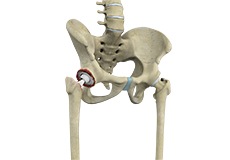
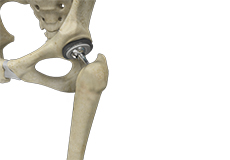
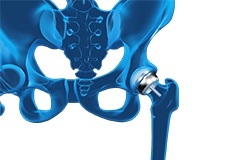
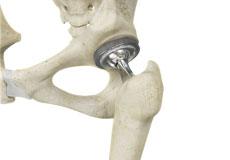
Total Hip Replacement
Total hip replacement is a surgical procedure in which the damaged cartilage and bone are removed from the hip joint and replaced with artificial components. The main indication for total hip replacement is arthritis.
-
Hip Resurfacing
The hip joint is also known as a ball and socket joint, where the ball (femoral head) of the thigh bone fits into the socket (acetabulum) of the pelvic bone.
-
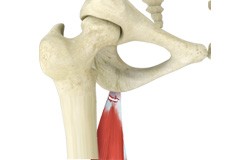
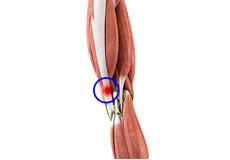
Hamstring Strain
A hamstring strain is an excessive stretch or tearing of hamstring muscles which are located at the back of the thigh. It is a common injury particularly seen in athletes who participate in sports activities that requires running, jumping, and kicking. During growth spurt the bones grow faster than the muscles.
-
Iliotibial Band (ITB) Syndrome
Iliotibial band syndrome is an overuse injury resulting from the inflammation of iliotibial band. Iliotibial band is a tough group of fibers that begins at the iliac crest of hip and runs along the outside of the thigh, to get attached to the outer side of the shin bone just below the knee joint. Its function is to coordinate with the thigh muscles and provide stability the knee joint.
-
Periacetabular Osteotomy
Periacetabular osteotomy is the surgical procedure indicated in hip dysplasia and it involves cutting the bone around the acetabulum so as to fit the head of the femur bone into acetabular socket. This method was developed and performed by Professor Reinhold Ganz and therefore it is also called as Ganz osteotomy.
-
Stryker Tripolar THA
Stryker Tripolar THA is a total hip replacement procedure using a special implant called an unconstrained tripolar implant or dual mobility acetabular component designed by Stryker. This implant was introduced to prevent instability caused by other types of implants.
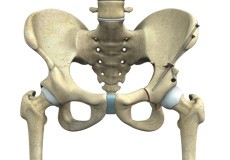
Hip Joint
The hip joint is the largest weight-bearing joint in the human body. It is also referred to as a ball and socket joint and is surrounded by muscles, ligaments, and tendons. The thigh bone or femur and the pelvis join to form the hip joint.
Any injury or disease of the hip will adversely affect the joint's range of motion and ability to bear weight.
The hip joint is made up of the following:
- Bones and joints
- Ligaments of the joint capsule
- Muscles and tendons
- Nerves and blood vessels that supply the bones and muscles of the hip
Bones and Joints
The hip joint is the junction where the hip joins the leg to the trunk of the body. It is comprised of two bones: the thigh bone or femur and the pelvis which is made up of three bones called ilium, ischium, and pubis. The ball of the hip joint is made by the femoral head while the socket is formed by the acetabulum. The Acetabulum is a deep, circular socket formed on the outer edge of the pelvis by the union of three bones: ilium, ischium, and pubis. The lower part of the ilium is attached by the pubis while the ischium is considerably behind the pubis. The stability of the hip is provided by the joint capsule or acetabulum and the muscles and ligaments which surround and support the hip joint.
The head of the femur rotates and glides within the acetabulum. A fibrocartilagenous lining called the labrum is attached to the acetabulum and further increases the depth of the socket.
The femur or thigh bone is one of the longest bones in the human body. The upper part of the thigh bone consists of the femoral head, femoral neck, and greater and lesser trochanters. The head of the femur joins the pelvis (acetabulum) to form the hip joint. Next, to the femoral neck, there are two protrusions known as greater and lesser trochanters which serve as sites of muscle attachment.
Articular cartilage is the thin, tough, flexible, and slippery surface lubricated by synovial fluid that covers the weight-bearing bones of the body. It enables smooth movements of the bones and reduces friction.
Ligaments
Ligaments are fibrous structures that connect bones to other bones. The hip joint is encircled with ligaments to provide stability to the hip by forming a dense and fibrous structure around the joint capsule. The ligaments adjoining the hip joint include:
- Iliofemoral ligament: This is a Y-shaped ligament that connects the pelvis to the femoral head at the front of the joint. It helps in limiting the over-extension of the hip.
- Pubofemoral ligament: This is a triangular shaped ligament that extends between the upper portion of the pubis and the iliofemoral ligament. It attaches the pubis to the femoral head.
- Ischiofemoral ligament: This is a group of strong fibres that arise from the ischium behind the acetabulum and merge with the fibres of the joint capsule.
- Ligamentum teres: This is a small ligament that extends from the tip of the femoral head to the acetabulum. Although it has no role in hip movement, it does have a small artery within that supplies blood to a part of the femoral head.
- Acetabular labrum: The labrum is a fibrous cartilage ring which lines the acetabular socket. It deepens the cavity, increasing the stability and strength of the hip joint.
Muscles and Tendons
A long tendon called the iliotibial band runs along the femur from the hip to the knee and serves as an attachment site for several hip muscles including the following:
- Gluteals: These are the muscles that form the buttocks. There are three muscles (gluteus minimus, gluteus maximus, and gluteus medius) that attach to the back of the pelvis and insert into the greater trochanter of the femur.
- Adductors: These muscles are located in the thigh which helps in adduction, the action of pulling the leg back towards the midline.
- Iliopsoas: This muscle is located in front of the hip joint and provides flexion. It is a deep muscle that originates from the lower back and pelvis and extends up to the inside surface of the upper part of the femur.
- Rectus femoris: This is the largest band of muscles located in front of the thigh. They also are hip flexors.
- Hamstring muscles: These begin at the bottom of the pelvis and run down the back of the thigh. Because they cross the back of the hip joint, they help in extension of the hip by pulling it backwards.
Nerves and Arteries
Nerves of the hip transfer signals from the brain to the muscles to aid in hip movement. They also carry the sensory signals such as touch, pain, and temperature back to the brain.
The main nerves in the hip region include the femoral nerve in the front of the femur and the sciatic nerve at the back. The hip is also supplied by a smaller nerve known as the obturator nerve.
In addition to these nerves, there are blood vessels that supply blood to the lower limbs. The femoral artery, one of the largest arteries in the body, arises deep in the pelvis and can be felt in front of the upper thigh.
Hip Movements
All of the anatomical parts of the hip work together to enable various hip movements. Hip movements include flexion, extension, abduction, adduction, circumduction, and hip rotation.